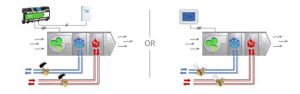
The application of this system is related to cases where we want to control the temperature of each space separately.
Also, using the coil system will prevent the transfer of contamination between rooms. Suitable applications of this system include: hotels, residential buildings, office buildings, hospitals, etc.
Advantages of fan coil:
The main advantage of a fan coil is that its piping system requires less space. It can also be operated with a chiller and central heating system. It can also be controlled separately to reduce energy costs. It allows each room to be controlled separately. Since this system can also be heated with low water temperatures, it is suitable for areas where heat generation is solely by solar panels. For the design of existing building facilities, piping and wiring a fan coil is simpler than the large ducts required for an all-air system.
Fan coil piping system:
Fan coil systems are divided into two types: two-pipe fan coil and four-pipe fan coil. A two-pipe fan coil has one inlet pipe and one return pipe. The cold or hot water supply pipe (depending on the season) to the fan coil is responsible for transporting water. Four-pipe fan coil units have two supply pipes and two return pipes. This allows hot or cold water to enter the fan coil at any time, depending on the need and control command.
Since it is often necessary to heat or cool different parts of the building simultaneously, the four-pipe fan coil unit is more commonly used due to its ability to provide simultaneous heating and cooling.
How to choose a fan coil:
Type:
Fan coils come in different types such as cassette, one-way or four-way, built-in ceiling, duct and floor fan coils, which are selected based on the type of use by designers.
Capacity:
When calculating the fan coil capacity, which is determined based on the total cooling load (sensible and latent) of each space, always try to base the fan coil capacity on the average speed.
Q: Building cooling load in (BTU/MIN)
M: Fan coil air flow in (CFM)
CP: Specific heat of air at constant pressure, which is a number equal to 0.018 in (BTU/ft3. °F)
TΔ: Temperature difference between the fan coil inlet and outlet air in degrees Fahrenheit
Sound level:
Sound level is one of the factors that must be taken seriously. The success or failure of the installation project may affect the final sound level, and this factor is often ignored. Other factors affecting the sound level include ceiling height, type of ceiling construction, acoustic rooms, and generally how the fan coil is placed and the type of motor and fan used.
When choosing a fan coil, you should also pay attention to points such as the dimensions of the device, its appearance, proper controllability, and its price.
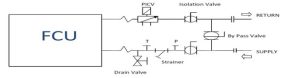
How a fan coil works:
The cold or hot water produced by the chiller or boiler is sent by pumps through risers to smaller diameter pipes to be directed to the fan coils (FCU). The FCU is basically a box with an internal fan that draws air from the space and passes it over a hot or cold coil to change the air temperature and then distributes this air into the space. Cold water enters the FCU and passes through a cooling coil (a set of thin tubes) and absorbs the heat from the air inside it. The cold water is heated, and as a result, the air throughout it is cooled. When the cold water leaves the cooling coil, it will have warmed up by about 5°C (53.6°F), reaching 12°C. The warmed cold water is then returned to the chiller evaporator through the return risers. The cold water is cooled again and is ready to circulate through the building and collect more heat load.